Follicular Adenoma
This website is expert resource on thyroid by world renowned expert on thyroid surgery Dr Sandeep Nayak at MACS Clinic, Bangalore, India.
We have tried to make this site as a comprehensive information source for all thyroid problems that may require surgery and other added treatments. We have detailed pages about problems different types of thyroid nodules and cancers like papillary carcinoma, follicular carcinoma, etc. This site is provided by the MACS Clinic and Dr Sandeep Nayak, one of the world’s most renowned thyroid surgeons operating out of major hospitals located in Bangalore, India. Dr Nayak is known for the development of robotic thyroidectomy technique called RABIT which is used for thyroid cancer surgery. This site is constantly updated with new information.
Overview
 A follicular adenoma is a common type of benign thyroid tumor that arises from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. These adenomas are typically non-cancerous, and while they may not pose an immediate threat to health, their presence can sometimes be concerning due to their potential to grow or cause symptoms. .
A follicular adenoma is a common type of benign thyroid tumor that arises from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. These adenomas are typically non-cancerous, and while they may not pose an immediate threat to health, their presence can sometimes be concerning due to their potential to grow or cause symptoms. .
Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a trusted name in thyroid surgery, explains:
“Follicular adenomas, although benign, require careful monitoring to ensure they don’t progress or cause unnecessary complications. Follicular adenomas can vary in size, and some may even cause noticeable swelling in the neck area. This diagnosis is confirmed by the FNAC test which shows level 2 Bethesda category.
It’s important that FNAC test is performed by an experienced radiologist and the reporting is done by a pathologist who regularly sees thyroid samples. While they often don’t produce symptoms, it’s crucial to differentiate them from more serious thyroid conditions, which require different approaches in diagnosis and treatment.”
Follicular adenomas are usually detected during routine check-ups or when symptoms prompt further investigation. Understanding the nature of these growths is key to managing them effectively.
Symptoms and Causes
Symptoms of follicular adenoma can range from mild to more noticeable signs, depending on the size and location of the tumor. Some common symptoms include:
Neck Swelling:
A visible lump or swelling in the neck is often one of the first signs.
Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing:
As the adenoma grows, it may press against the esophagus or windpipe, leading to discomfort.
Hoarseness:
Compression of the vocal cords by a growing adenoma can cause voice changes. This is very rare unless the adenoma becomes very huge.
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms:
In rare cases, a follicular adenoma may secrete thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms like rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and nervousness. This can be confirmed by thyroid nuclear scan which will tell if the nodule is hot or functioning more.

The exact cause of follicular adenoma is not well understood, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- A family history of thyroid disorders can increase the risk.
- Previous exposure to radiation, particularly in childhood, is a known risk factor.
- Lack of adequate iodine in the diet can sometimes lead to the formation of thyroid nodules, including adenomas.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing follicular adenoma involves several steps, including clinical evaluation, imaging, and pathology:
Physical Examination:
A thorough neck examination can reveal the presence of lumps or swelling.
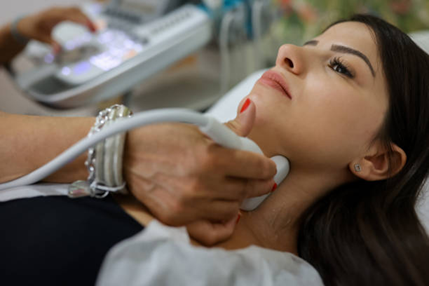
Ultrasound Examination:
Perform an ultrasound to evaluate the thyroid nodule’s size, shape, and characteristics. This imaging technique helps distinguish between solid and cystic nodules and assesses the likelihood of malignancy.
Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy:
Conduct an FNA biopsy to collect cells from the thyroid nodule for microscopic examination. This procedure helps determine whether the nodule is a benign follicular thyroid nodule or malignant. This procedure is usually done under ultrasound guidance to target the most representative part of nodule.
Thyroid Function Tests:
Evaluate thyroid hormone levels (T3, T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to determine thyroid function. These tests help detect whether the nodule is impacting hormone production.
Scintigraphy (Thyroid Scan):
Radioactive iodine or technetium is used to perform a thyroid scan. This method aids in the diagnosis of follicular adenoma by determining whether the nodule is:
- “hot” (producing excess thyroid hormones), or
- “cold” (non-functioning)
Follicular Adenoma Pathology Outlines:
Analyze the biopsy samples under a microscope to observe cellular patterns and characteristics. Follicular adenoma pathology outlines focus on identifying the uniform follicular cell arrangement, the presence of a capsule, and the absence of vascular or capsular invasion, which differentiates it from follicular carcinoma.
Have a Question?
Are you experiencing any of these symptoms or have concerns about thyroid health? If so, it’s essential to consult a trusted thyroid cancer specialist to determine the best course of action.
Follicular Adenoma Treatment Options
Managing follicular adenoma depends on several factors, including the size of the adenoma, the symptoms it causes, and the patient’s overall health.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of management, especially for small or asymptomatic adenomas:
1. Watchful Waiting:
Regular monitoring through physical exams and ultrasounds to observe any changes in the adenoma’s size or behavior.
2. Thyroid Hormone Suppression Therapy:
In some cases, patients may be prescribed thyroid hormone medication to suppress TSH production, potentially shrinking the adenoma or preventing further growth. This treatment is generally reserved for patients with multiple nodules or those with elevated TSH levels.
3. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA):
A thin needle is inserted into the nodule, and radiofrequency energy is applied to heat and destroy the tissue. RFA is particularly beneficial for patients who prefer to avoid surgery and effectively reduces symptoms and cosmetic concerns related to larger nodules.
4. Ethanol Injection Therapy:
Ethanol injection therapy involves injecting ethanol (alcohol) directly into the thyroid nodule to shrink it. This treatment is less commonly used but can be an option for patients who are not candidates for surgery.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery may be recommended if the adenoma is large, symptomatic, or shows signs of potential malignancy:
1. Lobectomy:
Removal of the affected lobe of the thyroid gland. This procedure is often sufficient if the adenoma is confined to one part of the thyroid.
2. Total Thyroidectomy:
Complete removal of the thyroid gland may be necessary if multiple adenomas are present or if there’s a concern for cancer.
3. Minimally Invasive Thyroid Surgery:
A surgical approach that uses smaller incisions to remove thyroid nodules or affected lobes. This technique reduces scarring and recovery time while effectively addressing the thyroid condition.
Have a Question?
Are you wondering if surgery is the right option for you? It’s crucial to discuss your concerns with a qualified thyroid surgeon who can guide you through the decision-making process.
Potential Side Effects and Complications of Follicular Adenoma Treatments
Thyroid Hormone Suppression Therapy:
May cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as increased heart rate, anxiety, or weight loss.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA):
Possible pain, swelling, or skin burns at the treatment site.
Ethanol Injection Therapy:
Risk of local pain, inflammation, or damage to surrounding thyroid tissue.
Lobectomy:
Possible hoarseness, low calcium levels (hypocalcemia), or need for thyroid hormone replacement if the remaining lobe doesn’t function adequately.
Total Thyroidectomy:
Requires lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy, with risks of hoarseness, hypocalcemia, or infection.
Regular follow-up and discussions with your healthcare provider ensure that any changes are promptly addressed, minimizing the risk of complications.
How to Reach Us
Each year, our center welcomes many patients from all corners of the globe. With our extensive experience, we have streamlined the process to make it effortless for you to visit Bangalore for your evaluation, scans, biopsies, and surgery all in one trip. For your convenience, a significant portion of the follow-up can be conducted through online consultations. Additionally, we are committed to assisting you with postoperative treatment in your home country or city, eliminating the need for you to return to Bangalore, India.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Follicular Adenoma Turn into Cancer?
A follicular adenoma is generally a benign thyroid nodule and does not turn into cancer. However, it’s essential to monitor the condition closely, as some nodules may have overlapping features with follicular carcinoma, which requires a different treatment approach.
Is Follicular Adenoma Hereditary?
How Often Should I Monitor Follicular Adenoma?
Will Follicular Adenoma Affect My Thyroid Function?
Can Lifestyle Changes Help Manage Follicular Adenoma?
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.