The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck. It plays a crucial role in regulating your metabolism, energy levels, and overall hormonal balance. This regulation is achieved by releasing thyroid hormones, such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). In normal functioning, it helps the smooth running of the systems within the body. However, thyroid problems can lead to an overactive or underactive thyroid, causing an imbalance that can negatively affect several body functions.

Thyroid problems, particularly hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can significantly affect a person’s fertility. According to Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a prominent expert in thyroid surgery, thyroid imbalances can disrupt hormonal balance, ovulation, and menstrual cycles in women, further complicating conception. Sometimes, thyroid problems may even result in complications during pregnancy.
In this blog, we will discuss how thyroid disorders can cause infertility, describe the symptoms, and look at the available treatment options to help deal with fertility problems caused by the thyroid.
The Role of the Thyroid in Reproductive Health
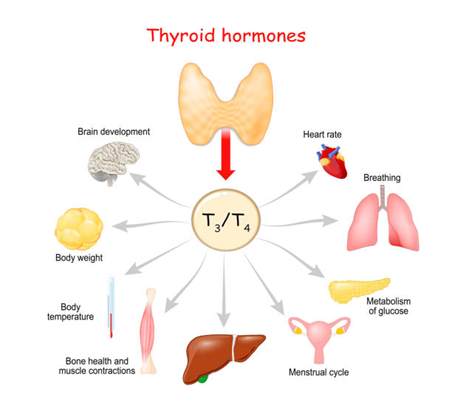
Most importantly, thyroid hormones exert a strong influence on the reproductive system by regulating other essential hormones involved in fertility. These hormones are necessary for women in the development of eggs and for men in the production of sperm. Furthermore, thyroid hormones regulate menstrual cycles and support early stages of pregnancy.
The thyroid and infertility in females are closely linked. Thyroid dysfunction in women may affect ovulation, which is essential for conception. For men, thyroid imbalances can lead to issues like reduced sperm count or motility, affecting their fertility. Maintaining balanced thyroid hormone levels is essential for optimal reproductive health. Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can interfere with these delicate processes.
How Hypothyroidism Affects Fertility
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone, leading to slowed metabolism and other bodily imbalances. This condition can significantly affect fertility, particularly in women, by disrupting the menstrual cycle and affecting ovulation.
In Women
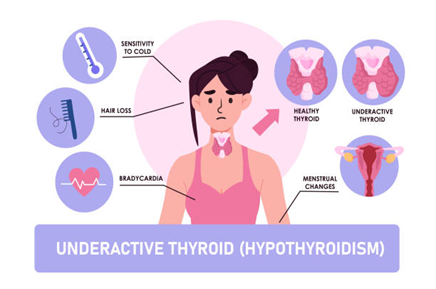
Hypothyroidism in women can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, heavy or prolonged periods, and anovulation (lack of ovulation). Without regular ovulation, the chances of becoming pregnant diminish. In some cases, hypothyroidism can even result in miscarriage if not properly managed during pregnancy.
Furthermore, hypothyroidism may also contribute to other reproductive issues, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is another condition that can impair fertility. The hormonal imbalance caused by hypothyroidism can lead to an overproduction of prolactin, a hormone responsible for lactation. Elevated prolactin levels can further disrupt the menstrual cycle and prevent ovulation, hindering fertility.
In Men
In men, hypothyroidism can affect sperm production and motility, reducing the likelihood of successful fertilization. Symptoms like low libido and erectile dysfunction can also occur due to low thyroid hormone levels. These fertility problems often go undiagnosed, as men may not immediately connect their thyroid health with reproductive issues.
How Hyperthyroidism Impacts Fertility
Hyperthyroidism, on the other hand, occurs when the thyroid produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, leading to an overactive metabolism. While it can cause weight loss and increased heart rate, it can also have profound effects on fertility.
In Women
Hyperthyroidism, in females, may cause or sometimes lead to irregular periods or the complete cessation of menstruation. This makes ovulation timing hard to predict, thereby limiting the chances of conception. Besides, hyperthyroidism may increase the risk for miscarriage and preterm birth if left without treatment.
Other complications for some women may include a condition called “thyroid storm,” a form of extreme hyperthyroidism that may present hazardous symptoms such as high fever, rapid heartbeat, and even organ failure. Thyroid storm is hazardous to pregnancy and needs immediate attention.
In Men
In the case of men, hyperthyroidism also brings about a decrease in sperm count and motility. Testosterone levels can be affected by the condition, which is essential in the production of sperm and overall fertility. Thus, it can be more difficult for men to father a child due to this condition.
Common Symptoms of Thyroid-Related Fertility Problems
Understanding the symptoms of thyroid-related fertility issues can help individuals recognize the underlying causes of their infertility. Some common symptoms of thyroid imbalances include:
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
- Heavy or light periods
- Fatigue or lethargy
- Weight gain or loss
- Difficulty conceiving
- Changes in libido
- Depression or mood swings
- Changes in skin texture or hair loss
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical advice from a qualified professional who specializes in thyroid disorders and fertility issues.
Treatment Options for Thyroid-Related Infertility

The good news is that both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can be treated, and fertility can be restored with proper management. Treatment options depend on the severity and type of thyroid disorder.
- Hypothyroidism Treatment:

The most common treatment for hypothyroidism is synthetic thyroid hormone replacement, such as levothyroxine. This helps restore thyroid hormone levels to normal and can help regulate the menstrual cycle and improve fertility.
- Hyperthyroidism Treatment:
For hyperthyroidism, treatment options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or, in some cases, surgery. By normalizing thyroid hormone levels, fertility can improve.
- Fertility Treatments:

In some cases, women may require additional fertility treatments like ovulation induction, in vitro fertilization (IVF), or intrauterine insemination (IUI) to help them conceive.
Conclusion
Thyroid disorders, whether hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can significantly impact fertility in both men and women. It is essential to address any thyroid imbalances promptly, as they can affect menstrual cycles, ovulation, and sperm production. Thankfully, with proper diagnosis and treatment, most thyroid-related fertility issues can be managed, giving couples a better chance at conception. Consult with an experienced specialist, such as Dr. Sandeep Nayak, who can provide expert guidance on managing thyroid health and improving fertility.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause thyroid problems?
Can someone with thyroid disease have a healthy married life and pregnancy ?
Yes. With proper treatment and regular monitoring, most people with thyroid disorders can lead a normal married life and have a healthy pregnancy.
How to conceive fast with thyroid?
At what age do thyroid problems start?
Can a thyroid test help diagnose infertility?
Reference links:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9829629/
https://www.verywellhealth.com/the-effects-of-pregnancy-on-the-thyroid-and-tsh-levels-3232932
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes and not for promotional use.

