Thyroid cancer and lung cancer are among the most widely discussed cancers today, though they affect very different organs. Thyroid cancer is generally known for its good prognosis and high survival rates when treated early. Lung cancer, on the other hand, is considered one of the most aggressive cancers, often detected at an advanced stage.
However, here’s where it becomes important: studies have shown that these two cancers may be connected. In some cases, thyroid cancer can spread to the lungs. In other situations, certain risk factors may overlap, making patients more vulnerable to both conditions.
“While thyroid cancer usually has excellent outcomes, it can sometimes spread to the lungs. Understanding this link allows patients and doctors to take timely steps for better management,” explains Dr. Sandeep Nayak, leading surgical oncologist in India at MACS Clinic.
What is Thyroid Cancer?
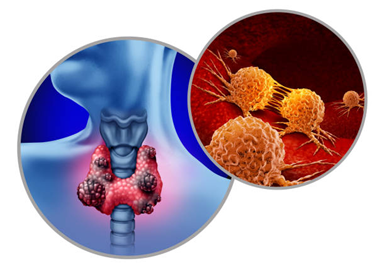
Thyroid cancer originates in the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ situated at the base of the neck. This gland controls metabolism and hormones that affect growth, energy, and overall health.
There are several types of thyroid cancer:
- Papillary thyroid cancer (most common and usually treatable)
- Follicular thyroid cancer
- Medullary thyroid cancer
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer (rare and aggressive)
Early detection often leads to excellent outcomes. Most patients do well with timely treatment, but the cancer can sometimes spread to other parts of the body.
What is Lung Cancer?
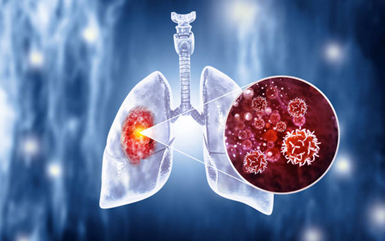
Lung cancer develops when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the lungs. It is one of the most common and serious types of cancer worldwide.
There are two major types:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) – accounts for most cases.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) – spreads more quickly.
Symptoms often include:
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
- Unexplained weight loss
Since these signs can appear late, lung cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage.
The Connection Between Lung Cancer and Thyroid Cancer

At first glance, the thyroid and lungs serve very different functions. Yet cancer can link them in two important ways:
- Metastasis (Spread of Cancer):
- Thyroid cancer can spread (metastasize) to the lungs.
- Similarly, lung cancer can rarely spread to the thyroid.
- Shared Risk Factors:
- Smoking, radiation exposure, and genetic factors may increase the chances of developing both.
Medical studies have shown that thyroid metastasis to the lung occurs in around 5–10% of advanced thyroid cancer cases. This is particularly seen in papillary and follicular thyroid cancers.
Is Having Thyroid Cancer a Risk Factor for Lung Cancer?
This is a common concern among patients. The simple answer:
- Thyroid cancer itself is not a direct cause of lung cancer.
- However, people with a history of thyroid cancer may need closer monitoring.
Why?
- Thyroid cancer can spread to the lungs, especially in advanced stages.
- Treatments like radiation for thyroid cancer may slightly increase the risk of second cancers, including lung cancer, though this is uncommon.
However, having thyroid cancer does not guarantee lung cancer, but it highlights the need for long-term follow-up care.
Treatment Options for Thyroid and Lung Cancer
Treatment choices depend on the type of cancer, its stage, and the overall health of the patient. Managing these conditions often requires a combination of therapies for the best results.
For Thyroid Cancer
- Surgery: This is the primary treatment option and involves removing part or all of the thyroid gland. It is usually highly effective in the early stages of cancer.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy (RAI): Often recommended after surgery, RAI helps destroy any remaining thyroid cancer cells in the body.
- Targeted Therapy: These medicines work by attacking specific mutations or pathways that fuel cancer growth.
- External Beam Radiation and Chemotherapy: Generally reserved for advanced or aggressive thyroid cancers that do not respond to standard therapies.
For Lung Cancer

- Surgery: Considered when the disease is detected early and confined to a limited area of the lung.
- Radiation Therapy: Delivers powerful energy rays to destroy cancer cells and may be administered on its own or in combination with other treatments.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs circulate throughout the body to target and attack cancer cells, especially when the disease has spread.
- Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy: Modern approaches that enhance the body’s immune system or focus on specific cancer cell changes to improve outcomes.
When Both Thyroid and Lung Cancer Are Present
Treatment becomes more complex and requires a multidisciplinary team of specialists. The goal is to create a plan that optimally balances surgery, radiation, and drug therapies for the patient.
Advanced cancer centers such as MACS Clinic provide comprehensive treatment options for both thyroid and lung cancers. With access to robotic and laparoscopic procedures, patients benefit from less invasive surgeries, quicker recovery, and precise cancer control.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Survival depends on several factors, including the stage of cancer, age, and overall health.
- Thyroid Cancer:
- Most patients, especially with papillary thyroid cancer, have excellent survival rates.
- Even when it spreads to the lungs, patients can live long with proper treatment.
- Lung Cancer:
- Survival rates are lower, particularly when the disease is diagnosed at a late stage.
- Advances in targeted therapy and immunotherapy are improving outcomes.
When thyroid cancer metastasizes to the lung, the disease may still be managed effectively for years with treatments like surgery, RAI, and targeted therapy.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
You cannot always prevent cancer, but you can lower risks.
- Quit smoking: The most critical step for lung health.
- Stay active: Regular exercise improves immunity and lung capacity.
- A balanced diet: Includes fruits, vegetables, and foods rich in antioxidants.
- Avoid radiation exposure: Only undergo medical scans when necessary.
- Regular check-ups: Significant if you have a history of thyroid cancer.
Prevention doesn’t guarantee safety but helps reduce the chances of serious illness.
Conclusion
The link between thyroid and lung cancer lies mainly in metastasis and shared risks. Thyroid cancer can spread to the lungs in some cases, but with timely treatment and close follow-up, patients often do well.
Innovative surgical methods, such as RABIT developed by Dr. Sandeep Nayak, are making treatment more effective and less invasive. Staying informed, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking prompt medical advice remain the best strategies for managing risk.

