Treatment – Overview
This page is developed under the guidance of Dr. Sandeep Nayak, an acclaimed surgical oncologist in India from MACS Clinic, Bangalore. He is recognised worldwide for his expertise in thyroid cancer surgery and for pioneering the minimally invasive RABIT technique for thyroidectomy. The page aims to provide accessible information to patients and their families, guiding them through the complexities of thyroid cancer treatment.
Thyroid cancer is a condition in which abnormal cells grow in the thyroid gland. It requires careful consideration of treatment options. This page outlines various treatment options for different types of thyroid cancers. These include the most common papillary thyroid carcinoma, follicular neoplasm and rarer forms like medullary and anaplastic thyroid cancers.
Have a Question?
Treatment Option Overview
Key Points
Different types of thyroid cancer treatments
The types of treatments include:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy, including radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy
- Thyroid hormone therapy
- Targeted therapy and Chemotherapy
New treatment options currently being tested in clinical trials:
- Immunotherapy
Side Effects of Thyroid Cancer Treatments
Follow-up Tests
Treatment Options for Stage I, II, and III Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Treatment for Stage IV (Metastatic) Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Treatments for Recurrent Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Treatment for Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Treatment for Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
Different Types of Thyroid Cancer Treatments

The types of treatments include:
Surgery
Surgery is the primary treatment for thyroid cancer. There are different types of surgical procedures that thyroid surgeons may use, including:
Lobectomy
Removal of the lobe of the thyroid gland affected by cancer. This is done only for cancers 1 cm or smaller. There are some centres practicing this for tumours up to 4 cm in size, however, the evidence for this is not strong enough. The surgeon does not remove the lymph nodes (lymph node dissection) as it is not indicated.
Near-total thyroidectomy:
Removal of the entire thyroid gland, except for a tiny part. This not preferred surgery anymore and should not be done.
Total thyroidectomy:
Removal of the entire thyroid gland. This is the most preferred surgery for thyroid cancers and in trained hands can be performed safely. During this procedure, the surgeon may perform lymph node dissection to check the spread of cancer cells.
Radio-iodine therapy and radiation therapy
Radio-iodine therapy is the main treatment after surgery for thyroid cancer. This is a form of internal radiotherapy.
Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy:
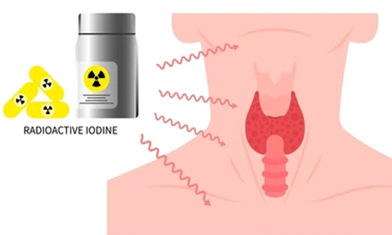 Follicular cancer of thyroid and papillary thyroid carcinoma may be treated with radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy. This involves taking RAI by mouth, which thyroid tissue absorbs. It destroys cancer cells without harming other tissues. A small test dose is given before the complete RAI treatment to determine if the tumor absorbs iodine.
Follicular cancer of thyroid and papillary thyroid carcinoma may be treated with radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy. This involves taking RAI by mouth, which thyroid tissue absorbs. It destroys cancer cells without harming other tissues. A small test dose is given before the complete RAI treatment to determine if the tumor absorbs iodine.External radiation therapy
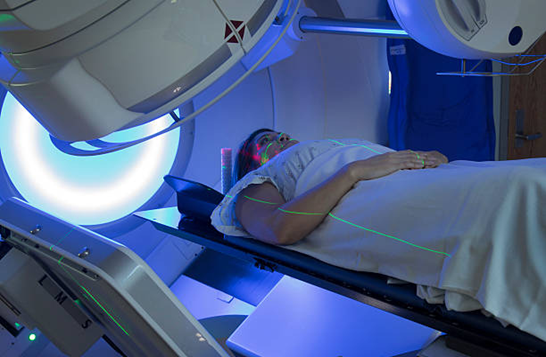 Employs a machine outside the body to direct radiation toward the area of the body with cancer. This is rarely indicated in thyroid cancers. It is used in rare situations where surgery is not possible.
Employs a machine outside the body to direct radiation toward the area of the body with cancer. This is rarely indicated in thyroid cancers. It is used in rare situations where surgery is not possible.Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill or stop cancer cells from growing or dividing. The method of administering chemotherapy depends on the type of cancer. Chemotherapy is not effective in thyroid cancers, unless it is thyroid lymphoma (type of blood cancer affecting the thyroid).
Thyroid Hormone Therapy
The thyroxine hormone which is produced by normal thyroid gland has an action on thyroid cancer. It suppresses its growth. For this reason, it is used at a higher dose then normal to control thyroid cancer. This works both as a replacement of the hormone and treatment to control cancer. Thyroid hormone is given as tablet that is to be taken once daily.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy involves using drugs or substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells. These are used rarely especially when no other treatment is available. There are different types of targeted therapy:
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy works by blocking signals required for tumors to grow. Sorafenib, vandetanib, lenvatinib, cabozantinib, larotrectinib, selpercatinib, pralsetinib, and entrectinib are all tyrosine kinase inhibitors used to treat advanced thyroid cancer.
- Protein kinase inhibitor therapy works by blocking proteins necessary for cell growth and may kill cancer cells. Trametinib and dabrafenib are examples of protein kinase inhibitors used to treat anaplastic thyroid cancer in patients with a certain mutation in the BRAF gene.
Need clarity on thyroid cancer treatment? Consult experienced thyroid cancer specialists for personalized advice.
Follow-up Tests
 Follow-up tests or checkups are necessary after cancer treatment. They help doctors evaluate treatment effectiveness and make decisions about continuing, modifying, or stopping treatment. The doctors may repeat these tests periodically after treatment ends. The follow-up tests also assist in monitoring your condition and checking for cancer recurrence.
Follow-up tests or checkups are necessary after cancer treatment. They help doctors evaluate treatment effectiveness and make decisions about continuing, modifying, or stopping treatment. The doctors may repeat these tests periodically after treatment ends. The follow-up tests also assist in monitoring your condition and checking for cancer recurrence.Have a Question?
Treatment Options for Stage I, II, and III (localized/regional) Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Treatment for stage I, II, and III (localized/regional) papillary thyroid carcinoma and follicular thyroid cancer may include:
Surgery (thyroidectomy or lobectomy) and lymph node dissection
RAI therapy
Hormone therapy
Treatment choice depends on factors like cancer stage, patient’s age, and health.
Treatment Options for Stage I, II, and III (localized/regional) Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer
When cancer spreads to other body parts, like the lungs and bones, it is still treatable. However, palliative lung and bone metastases treatments are available. They can help relieve follicular and papillary thyroid cancer symptoms and improve quality of life.
For stage IV (metastatic) papillary thyroid carcinoma and follicular thyroid cancer, treatment may include:
For tumors that absorb iodine:
Total thyroidectomy and lymph node dissection
RAI therapy
Hormone therapy
For tumors that do not absorb iodine called TENIS syndrome (thyroglobulin elevated negative iodine scintigraphy:
Total thyroidectomy and lymph node dissection
External radiation therapy
Hormone therapy
Targeted therapy using a tyrosine kinase inhibitor such as Lenvatinib or Sorafenib.
Surgery to remove cancer from areas where it has spread.
Clinical trials of chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are also available.
Treatments for Recurrent Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer:
Surgery to remove the tumor, with or without radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy.
RAI therapy.
External or intraoperative radiation therapy may be used as palliative therapy.
Chemotherapy.
Targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Clinical trials of targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Treatment for Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer can be either localized or advanced. If the cancer has spread to nearby muscles in the neck, it’s considered localized. Conversely, if it has spread to other parts of the neck or body, it’s classified as advanced or metastatic.
Treatment for localized medullary thyroid cancer can include:
Total thyroidectomy with lymph node dissection.
External radiation therapy can be an option for recurrent thyroid cancer.
Treatment for advanced medullary thyroid cancer may include:
Targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Chemotherapy as palliative therapy for symptom relief.
Treatment Options for Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer:
Total thyroidectomy or tracheostomy as palliative therapy.
External radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy, and targeted therapy with protein kinase inhibitors for patients with BRAF gene mutation.
Don’t delay; take action against thyroid cancer today. Start your journey to recovery now.
How to Reach Us
Each year, our center welcomes many patients from all corners of the globe. With our extensive experience, we have streamlined the process to make it effortless for you to visit Bangalore for your evaluation, scans, biopsies, and surgery all in one trip. For your convenience, a significant portion of the follow-up can be conducted through online consultations. Additionally, we are committed to assisting you with postoperative treatment in your home country or city, eliminating the need for you to return to Bangalore, India.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the recovery time after thyroid cancer surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and individual factors. However, most people can return to normal activities within a few weeks to a month.
Can thyroid cancer come back after treatment?
Thyroid cancer can recur after treatment. However, regular follow-up care and monitoring can help detect recurrence early, improving the chances of successful treatment.
What is the survival rate for thyroid cancer?
The survival rate for thyroid cancer is generally high, especially if the cancer is diagnosed and treated early.
Do I need to follow a special diet after thyroid cancer treatment?
There’s no specific diet for thyroid cancer. However, a healthy, balanced diet can support overall well-being during and after treatment. Iodine free diet is advised only before radioiodine therapy.
Can I lead a normal life after thyroid cancer treatment?
Yes, many patients lead normal, fulfilling lives after thyroid cancer treatment. Your medical team will guide you in managing any ongoing concerns.